PowerShell and REST APIs: A Practical Guide
PowerShell’s ability to interact with REST APIs (Representational State Transfer Application Programming Interfaces) opens a world of possibilities for your scripts. In this article, we’ll provide practical examples of how you can use PowerShell to interact with REST APIs and best practices to follow.
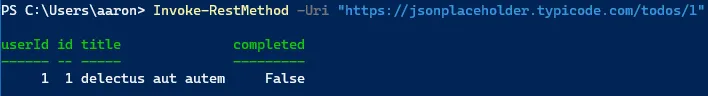
Example using Invoke-RestMethod GET
Understanding REST APIs
A REST API allows different systems to exchange data using HTTP methods such as GET, POST, PUT, DELETE, etc. REST APIs return data in various formats, with JSON and XML being the most common.
Making GET requests
One of the most common operations when working with REST APIs is making GET requests to retrieve data. Use the Invoke-RestMethod cmdlet in PowerShell to make GET requests:
# Making a GET request
$url = "https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/todos/1"
$response = Invoke-RestMethod -Uri $url
# Output the response
$responseThis will return details of a todo item.
Making POST requests
POST requests are used to send data to a REST API. Here’s an example of how to make a POST request with PowerShell:
# Making a POST request
$body = @{
title = "foo"
body = "bar"
userId = 1
} | ConvertTo-Json
$response = Invoke-RestMethod -Method Post -Uri 'https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts' -Body $body -ContentType 'application/json'
# Output the response
$responseThis script sends a POST request to the placeholder API and outputs the response.
Error handling
When working with REST APIs, it’s important to handle errors correctly. Use try-catch blocks to handle exceptions that might occur:
# Making a GET request with error handling
try {
$url = "https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/todos/1"
$response = Invoke-RestMethod -Uri $url
$response
} catch {
Write-Error "An error occurred: $_"
}REST APIs and PowerShell: best practices
Here are some best practices when working with REST APIs in PowerShell:
- Always Use Error Handling: APIs can fail for various reasons, always implement error handling in your scripts.
- Secure Sensitive Data: Never include sensitive data like API keys directly in your scripts. Consider using secure strings or Windows Credential Manager to handle this.
- Pagination Handling: Many APIs limit the amount of data returned in a single request. Be sure to handle pagination in your scripts.
Conclusion
PowerShell’s capability to interact with REST APIs greatly enhances its versatility, allowing your scripts to interact with thousands of web services.
More resources
- Invoke-RestMethod | learn.microsoft.com
- {JSON} Placeholder | jsonplaceholder.typicode.com
- Free fake API for testing and prototyping.